Cryosurgery is the use of extreme cold in surgery to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue; thus, it is the surgical application of cryoablation. The term comes from the Greek words cryo (κρύο) (“icy cold”) and surgery (cheirourgiki – χειρουργική) meaning “hand work” or “handiwork”. Cryosurgery has been historically used to treat a number of diseases and disorders, especially a variety of benign and malignant skin conditions.
Uses
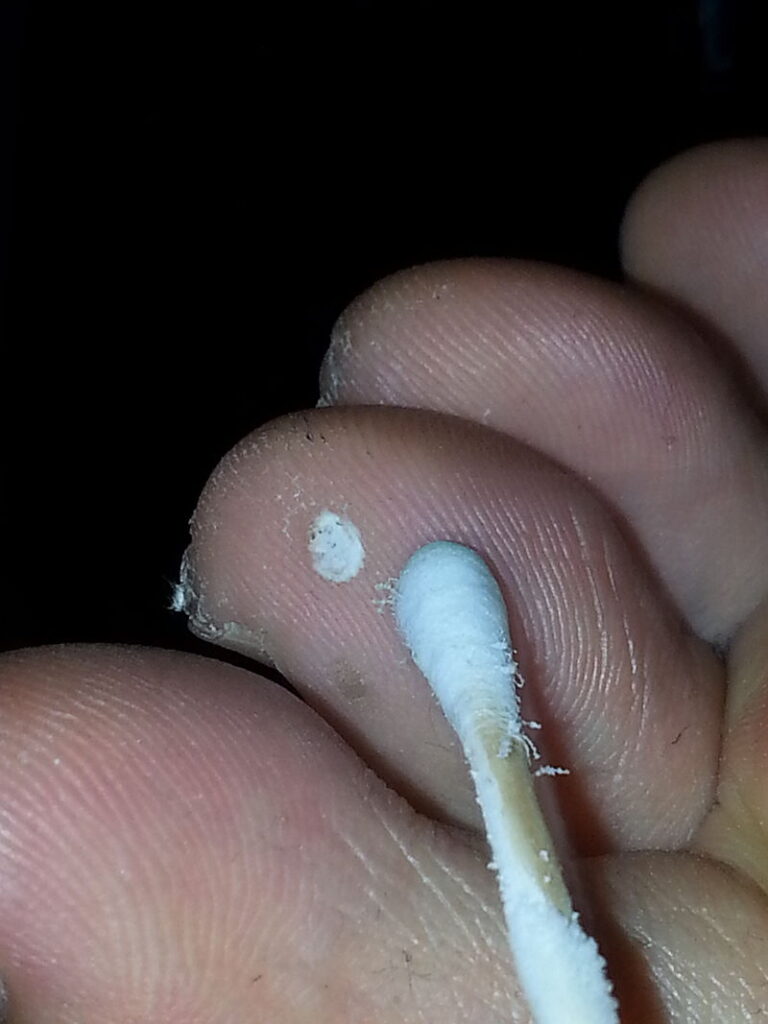
Warts, moles, skin tags, solar keratoses, molluscum, Morton’s neuroma and small skin cancers are candidates for cryosurgical treatment. Several internal disorders are also treated with cryosurgery, including liver cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, oral cancers, cervical disorders and, more commonly in the past, hemorrhoids. Soft tissue conditions such as plantar fasciitis (jogger’s heel) and fibroma (benign excrescence of connective tissue) can be treated with cryosurgery.
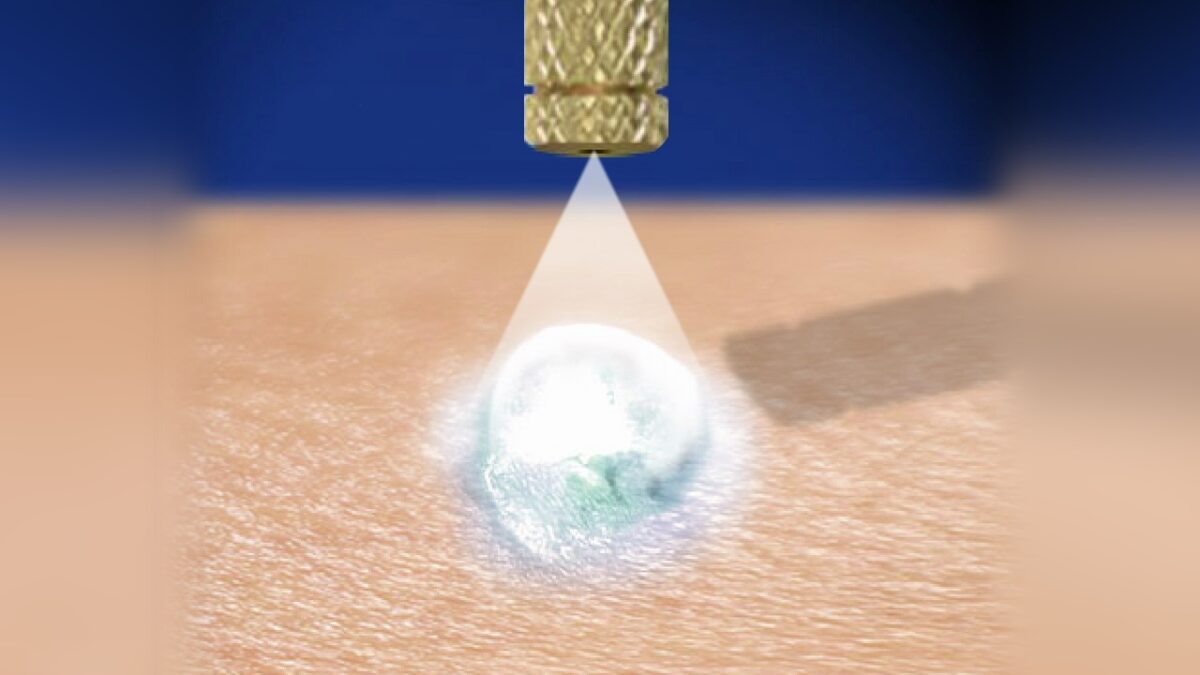
Cryosurgery works by taking advantage of the destructive force of freezing temperatures on cells. When their temperature sinks beyond a certain level ice crystals begin forming inside the cells and, because of their lower density, eventually tear apart those cells. Further harm to malignant growth will result once the blood vessels supplying the affected tissue begin to freeze.
Cryosurgery is used to treat a variety of benign skin lesions including:
- Acne
- Warts (including anogenital warts)
- Dermatofibroma
- Hemangioma
- Keloid (hypertrophic scar)
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Myxoid cyst
- Pyogenic granuloma
- Seborrheic keratoses
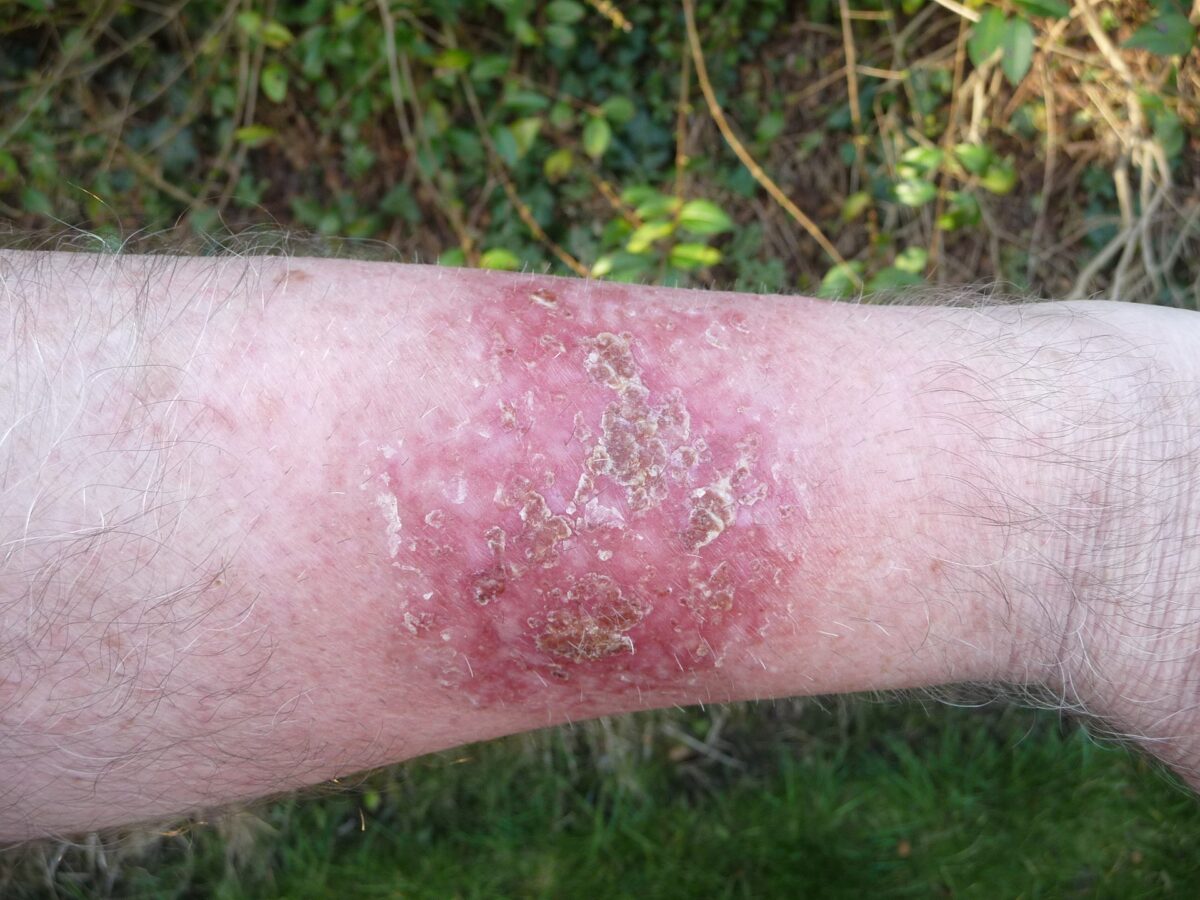
- Skin tagsCryosurgery may also be used to treat low risk skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma but a biopsy should be obtained first to confirm the diagnosis, determine the depth of invasion and characterize other high risk histologic features.
Source: Wikipedia

Leave a Reply